Alfalfa
(Medicago sativa)
Hay Grown the Right Way
United States Alfalfa hay is used both domestically and world wide as the basis of a healthy Dairy/ Beef cow and horse diet. More and more this high protein and high fiber feed option is finding a home overseas feeding other animals such as goats, sheep, Camels, and pigs.
Alfalfa can be grown throughout the world as forage for cattle and specific horse needs, and is harvested mostly as a hay product. Properly harvested western states alfalfa has high feeding value relative to other common hay crops. When alfalfa is grown on soils where it is well adapted, alfalfa is often the highest-yielding forage plant.
In most climates, alfalfa is cut three to four times a year, but it can be harvested up to 10 times per year in Arizona and southern California. Total yields are typically around eight tones per hectare (four short tons per acre) in temperate environments, but yields have been recorded up to 20 T./ha (16 tons per acre).

Growing Regions
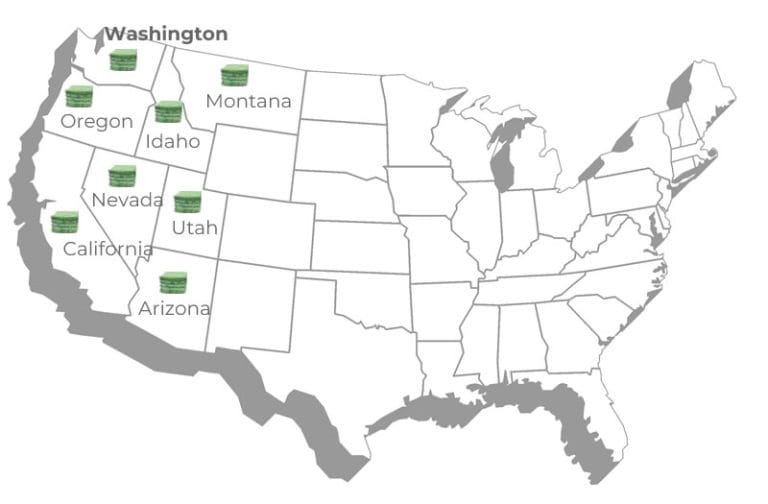
Alfalfa hay is grown in several regions across the United States. The western states, such as California, Arizona, Utah, Nevada, Idaho, Washington, Oregon, and Montana, are major producers of alfalfa hay for exporters. These regions benefit from arid and semi-arid climates, with access to irrigation systems for water supply, which is crucial for successful alfalfa cultivation.
Detailed overview
Nutritional Value:
Alfalfa hay is highly valued for its exceptional nutritional profile. It is rich in protein, essential amino acids, vitamins (including A, D, E, and K), and minerals (such as calcium, magnesium, and potassium). The balanced nutrient composition of alfalfa hay supports the growth, development, and overall health of livestock.
Forage Quality:
Alfalfa hay is recognized for its high forage quality. The plant's leafy portions, which have a higher protein content, are highly sought after. Farmers and ranchers carefully manage harvest timing to maximize the nutritional value and palatability of the hay.
Multiple Cuttings:
Alfalfa is a perennial plant that can be harvested multiple times during the growing season. In the United States, it is common to have three to five cuttings of alfalfa hay per year, depending on local growing conditions and management practices. This ensures a continuous supply of high-quality forage.
Economic Importance:
The production and sale of alfalfa hay significantly contribute to the agricultural economy in the United States. It provides income for farmers and supports the livestock industry, as well as related sectors such as hay exporters, feed manufacturers, and transportation.
Environmental Benefits:
Alfalfa has positive environmental attributes. Its deep root system helps improve soil health, reduce erosion, and enhance water infiltration. It also has the ability to fix nitrogen, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers in subsequent crops.
Alfalfa hay’s nutritional value, adaptability to different regions, and economic significance make it a crucial component of the livestock industry in the United States. The continued cultivation and production of alfalfa hay ensure a reliable supply of this nutritious forage product for livestock feed, supporting the well-being of animals and the success of farmers throughout the world.












